After we develop fruit timber, we all know we’re creating one thing scrumptious. Bugs perceive the identical factor, which ends up in an unwelcome military of pests consuming and affecting the fruit you develop. How do you eliminate these bugs with out utilizing dangerous sprays and coverings? Listed below are some ideas for figuring out bugs on fruit timber and controlling them organically.
The next is an excerpt from The Holistic Orchard by Michael Phillips. It has been tailored for the online.
Discovering Bugs On Fruit Timber
Studying to determine who’s who after which zeroing in on the when and the place of pest vulnerability (based mostly on household groupings) defines the crux of the matter in the case of bugs within the orchard. There are some useful ones and some deservedly infamous ones, however most species are in fact completely harmless. Detailed specifics in regards to the chosen few at your website might be discovered within the relevant fruit sections and in tree fruit guides listed within the sources. Our immediate aim is to grasp tips on how to stability potential pest conditions.
Figuring out Indicators of Insect Injury
Insect consciousness begins with paying consideration. Seeing early indicators of chewing on the sides of a bud or a light-deflecting pinprick (indicative of a feeding sting or an inserted egg) on creating fruit ought to put you on alert. Probing for particulars past this primary impression results in discovering a tiny caterpillar curled inside the sepal leaves on the base of a flower bud or searching for suspected culprits when cool morning dew finds curculios sluggish however not but in hiding.
One grower in Nebraska couldn’t determine what was consuming the leaves on his cherry timber . . . till he went out at night time with a flashlight and located that june bugs had come up from the bottom to feed with abandon. Various things will occur elsewhere—what’s fixed is the necessity to discern what’s truly happening so you’ll be able to then take clever measures to obtain a cheerful decision.
Distinguishing Fruit Scars

A russeted, fan-shaped scar speaks to the presence of plum curculio within the orchard. The feminine makes a crescent reduce above every inserted egg as a method of stopping fruit cells from crushing her reproductive artistry. Seeing scars on maturing fruit signifies that the apple gained the race. Photograph courtesy of NYSAES.
Insect harm to fruit gives an necessary studying alternative. The power to tell apart one fruit scar from one other most of the time reveals who’s actually behind the deed. Consulting with an skilled grower or Extension adviser, taking a look at regional pest guides, and browsing the phrases on this e-book are all instruments for getting your detective credentials so as.
Understanding the title of the responsible get together—if certainly the injury is important and thus requires particular motion within the subsequent rising season—results in studying about the life cycle of a specific pest. This in flip reveals factors of vulnerability the place trapping, repelling, sure beneficial allies, and specific spray methods have relevance.
Managing the State of affairs
However first let’s do the numbers. You want perspective to know the distinction between tolerable injury and a pest scenario quickly ratcheting uncontrolled. Analysis that tracked the injury executed in wild apple timber in Massachusetts over a twenty-year interval provides a reasonably correct image of what’s on the market.
Plum curculio and apple maggot fly can afflict as a lot as 90 % of the fruit in a nasty 12 months, with codling moth and one in every of its shut cousins getting digs into about half of those but once more. Extra injury from all different fruit-feeding pests tallies beneath 10 %. . . not one thing to get involved about by any means.
Overmanaging this case to have all fruit left untouched can have far too nice an affect on helpful populations and thereby induce extra pest challenges. It’s not well worth the expense or craziness of doing this. Decide your must-do priorities round these vital pests and grant {that a} small portion of the crop belongs to the pure world. The idea of stability works each methods.
Bugs on Fruit Timber: Who, What, and When
Each insect goes by means of a molting cycle that begins from the egg. The larval and pupal phases subsequently lead on to maturity and the reproductive urge. Injury to fruit timber is to both the foliage or the fruit itself. A few of this consists of grownup feeding, however most of the time it’s the egg hatching out a really hungry caterpillar or grub. Let’s have a look at household groupings inside the insect world related to orcharding as a fast technique of getting a deal with on potential pest conditions.
The aim right here just isn’t a lot entomological precision as figuring out related patterns to discern attainable responses to a pest dynamic deemed unacceptable.
The Orchard Moth Advanced
Each fruit grower will expertise the orchard moth complicated in some kind or one other. This ubiquitous drive can contain dozens of species, nevertheless it all the time means tiny caterpillars munching away on some half of the tree. Inside-feeding larvae go for the seeds in creating fruit, usually risking a mere twenty-four hours of weak leaf publicity earlier than getting safely tucked away inside.
Search for a small gap within the facet of the fruit and infrequently within the calyx finish from which orange-brown frass (poop) protrudes. Floor-feeding larvae are content material to nibble upon the pores and skin of the fruit, hiding beneath an overarching leaf or the place two fruit contact. Many of those are second-generation leaf curler species, which within the spring larval section had been intent on feeding on buds and unfurling leaf tissue. Any end resulting fruit injury at this early stage usually seems as corky indentations.
Moths on Fruit Timber
Let’s key in on this generational idea, for therein lies each the amplification of the moth problem and the timing of extraordinarily focused options. A given species overwinters as a hard-to-find egg mass, maybe as larvae (in a dormant state identified as diapause), some in a pupal cocoon, and a few even as grownup moths the place delicate winters enable for feeding and procreation. Location specifics differ as effectively, however principally orchard moths favor laying eggs on leaves and twigs the place larvae can subsequently feed.
These go on to seek out some secluded place to pupate: in crevices within the bark, litter on the orchard flooring, or sheltered nooks offered by a close-by fence or wall. A method or one other, with grownup emergence in spring depending on the event phases nonetheless to be achieves, first flight takes place when females get impregnated after which proceed to put eggs on the brand new season’s development.
That hatch initiates what is taken into account to be the primary era of the orchard 12 months – restrict this era and all subsequent generations might be fewer in quantity. Some species are content material with a single spherical of motion, whereas others will obtain as many as 5 or 6 generations of egg laying and larval feeding within the prolonged rising season of hotter climes.
The vulnerability factors with moths lie in grownup attraction across the occasions of feeding and mating, the necessity for eggs to breathe, larval ingestion and/or contact with organic toxins, and exposing pupae hiding on the tree trunk for bodily destruction.
Managing Fruit Flies
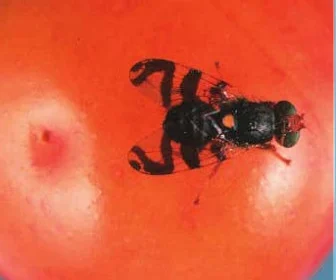
The cherry fruit fly assaults cherries all through the jap half of North America. Don’t fear, nevertheless – carefully associated cousins will discover the remainder of you! Photograph courtesy of NYSAES
Fruit-oriented flies have an effect on chosen fruits throughout the spectrum. Fly larvae are known as maggots, which I count on reveals the grotesque scene about to be revealed. The feminine grownup lays her eggs straight into the yielding flesh of ripening fruit, with particular choice by maggot fly species for apple, cherry, blueberry, and so forth. All such fruit turns into a maggoty mess of meandering tunnels and decay.
Feeding attractants are used to govern grownup flies to a lethal meal as an alternative, together with sticky sphere traps that promise the proper nursery for junior on which to put an egg. Soil pupation suggests extra vulnerability factors. Choose up early drops biweekly to forestall larvae from ever moving into the bottom.
Establishing A Clear Beginning Gate
Spraying the bottom beneath badly infested timber with Beauveria bassiana in fall may help reestablish a clear beginning gate: These parasitic fungi eat the fly pupae ready within the soil for subsequent season. Much more intentionally, plant a Dolgo crab tree to attract apple maggot flies in drove…use this as a entice tree to guard different apples, and the apply helpful nematodes in early fall (the Steinernema feltiae species is advisable for AMF) to hunt out the pupae within the floor beneath.
Sticking it to Sawflies
Sawflies are a unique class of critter altogether. Wasp points appear to have been included with fly-like habits on this insect, leading to a pollinator that in its larval kind simply occurs to bore into creating fruit or strip gooseberry branches of all greenery. Pear slugs (aka pear sawflies) look just about like fleshy blobs designed to skeletonize leaves. The vulnerability factors right here like with sticky card traps, desiccants like insecticidal cleaning soap and diatomaceous earth, and understanding exactly when a sure organic toxin will are available in contact with apple sawfly larvae shifting from a primary fruitlet to the subsequent.
The Bountiful Beetle
The factor about hard-backed beetles is that almost all of those species pupate within the soil. (People who go for wooden problem will get a separate designation.) Most notorious of all are the curculios, which decimate most any tree fruit within the jap half of North America. Repellents kind the spine of an natural plan for coping with these small weevils, with entice timber offering an efficient diversion to curtail an in any other case extended window of exercise. Relevant natural spray choices together with ground-level methods turn into cost-effective when a species can basically be funneled to far fewer unprotected timber.
Extra innocuous types like earwigs and click on beetles contribute again to the ecosystem, reminding me that tolerance has a spot. The accompanying sidebar directed at Japanese beetle is that this e-book’s instance of taking a specific pest by means of the organic wringer with a view to absolutely perceive what all is likely to be executed. Rose chafers are famous for having related needs for peaches. Out west, search for inexperienced fruit beetles rising from unturned (massive clue, proper there!) manure pile to wreak havoc on close by tender fruits.

Inexperienced june beetles have an affinity for apples and all stone fruits, whether or not immature or absolutely ripe. Feeding injury tends to be sporadic throughout southeastern states and into the Decrease Midwest. Photograph courtesy of NYSAES.
Eliminating Fruit Tree Borers
We blur species strains in mentioning the unspeakable evil executed by fruit tree borers. The rationale for lumping sure beetles with sure moths applies across-the-board injury to wooden tissue. Grub consumption of cambium and sapwood ultimately does in entire timber. Bodily inspection and removing entails quite a lot of work in your knees with a knife or related grub-seeking took like a drill spade bit.
Among the moths will be deterred by pheromone trapping, however decreasing beetle numbers usually entails limiting close by different hosts. Sending a military of parasitic nematodes into badly infested bark tissue by way of mudpack could rectify excessive conditions…and even if you happen to lose a well-liked tree, you might in the end save others by having eradicated the subsequent spherical of destruction.
Botanical trunk sprays made with pure neem oil are particularly promising, appearing as an oviposition repellent and including a component of insect development inhibition to all such borer wars.
True Bugs: Fruit Connoisseurs
True bugs exhibit an occasional hankering for fruit. These embrace assorted plant bugs, stink bugs, mullein bugs, apple purple bugs, and hawthorn darkish bugs. Typical suggestions for eradicating the alterative plant habitat for such bugs from the orchard environs go in opposition to a variety plan meant to draw and maintain necessary beneficials. Bug injury usually takes the type of a feeding sting, which develops into brownish tough blotches and even outright dimples on the pores and skin of the fruit. Pure neem oil will deter feeding and interrupt the molting cycle on all these guys, which – in truth – are hardly ever an all-out drive of devastation.
Uncommon Arrivals: Insect Erratica
I’ll point out a number of insect erratica, as sure regional curveballs can and do present up from time to time. The leaf-curling midge is a tiny fly whose larvae set again younger apple tree development by tightly curling terminal leaves on the ends of shoots. Much less photosynthesis means much less development. Pink-lumped caterpillars seemingly are Moths from Mars that assault apple, pear, cheery, and quince, defoliating total branches in just some days in late summer time…Pear thripsassault all deciduous fruit timber by feeding on flower clusters, inflicting a shriveled, nearly scorched look if the clusters don’t fall off the tree altogether.
Early-season neem oil purposes will forestall the vast majority of thrips invasions. Scale bugs are like tree barnacles in that they choose everlasting feeding sits on department twigs and limbs. Closely infested timber seem like present process water stress, with leaves yellowing and dropping. Parasitic wasps usually hold scale in examine (use a magnifying glass to search for holes drilled by means of the exhausting shell of mature scale), so until you’ve chosen to kill all the pieces in sight, don’t count on a lot bother from with San Jose or oystershell scale.
Foliar Feeders

Tarnished plant bug injury to buds and creating fruit is usually minimal – offered these bugs should not pushed up into the fruit timber by exuberant mowing of all close by floor cowl in spring. Photograph courtesy of Alan Eaton, College of New Hampshire.
Final however removed from least we should give heed to the foliar feeders. Permitting mites, aphids, psylla, and leafhoppers to run amok can set again tree vigor significantly. The excellent news is that a lot of that is certainly taken care of by quite a few helpful species given a little bit time. Business orchardists have way more issues with soft-bodied invaders as a result of lots of the chemical toxins used for vital pests kill the great guys that will in any other case checkmate foliar feeders, thus growing these types of issues dramatically.
Relying On Pure Dynamics
It’s far less complicated to depend on pure dynamics like predator mites to get the job executed. You’ll be able to pinch aphid infestations off terminal shoots on younger timber if mandatory, or shut personal the ant freeway by making use of sticky goo to plastic wrap on the trunk. If a sure plum selection seems overwhelmed by honeydew secretions from aphids and thus accompanying sooty molds cowl many of the cover, I depend on pure neem oil purposes (made at a 0.5 % focus each 4 to seven days) on that individual tree whereas an particularly extreme drawback persists.
Wooly, rosy, or plan inexperienced…aphids don’t like neem. Leafminers (the larvae of a small moth) tunnel into the mobile layers of the leaf to feed, however you’ll hardly ever see a lot of this injury in a house orchard as a result of sure braconid wasps know their responsibility. That’s the rub in a way…we truly want low variety of foliar feeder populations to take care of useful species to a enough diploma to maintain those self same foliar feeders in stability.
Advisable Reads
Crops & Pests: Will Bonsall’s Recommendation on “Wee Beasties” within the Backyard

