The world is already greater than 1 °C hotter on common than it was earlier than industrial occasions, owing to greenhouse gases launched from human actions. And that worth is rising. The Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC) tasks that there’s at the least a 50% probability that long-term world warming will overshoot 1.5 °C within the subsequent decade, even with bold emissions cuts.
That issues as a result of this goal is written into the 2015 Paris local weather settlement. Breaching it’ll set off questions on what must be finished to fulfill the settlement’s purpose — to curb human-induced local weather change. For instance, its intention of “pursuing efforts to restrict the temperature enhance to 1.5 °C” would then imply taking motion to reverse world warming, not simply stopping it — a a lot larger demand. A breach may also inevitably immediate assessments of the noticed impacts of exceeding 1.5 °C.
It would come as a shock, then, to listen to that the Paris assertion incorporates no formally agreed approach of defining the current stage of worldwide warming. The pact doesn’t even outline ‘temperature enhance’ explicitly and unambiguously. With out an agreed metric, there could be no consensus on when the 1.5 °C stage has been reached. That is prone to lead to distraction and delay simply on the level when local weather motion is most pressing.
Is it too late to maintain world warming beneath 1.5 °C? The problem in 7 charts
A key subject is that world temperatures don’t enhance easily. The temporary ups and downs that happen over weeks to years owing to pure local weather variability (induced, as an example, by El Niño occasions and the results of gases given off by volcanic exercise) are superimposed on the long-term warming pattern from human influences. For instance, the worldwide imply temperature rise exceeded 1.5 °C briefly for a month or extra in 2016, 2017, 2019, 2020 and 2023.
So far as the Paris settlement is anxious, it’s acknowledged that such temporary heat spells don’t depend as breaching 1.5 °C. And even an anomalously heat 12 months wouldn’t achieve this. The World Meteorological Group (WMO) predicts there’s a 66% probability that the worldwide imply temperature extra will go above 1.5 °C for at the least one 12 months within the subsequent 5 years1. Nevertheless, even that is prone to be a brief anomaly.
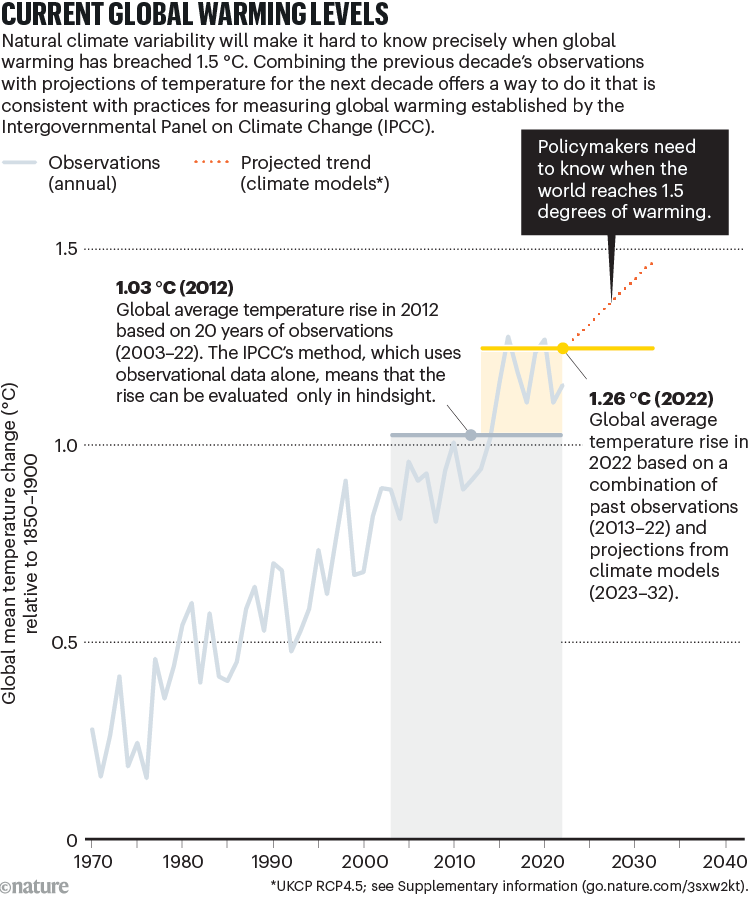
What would depend as passing 1.5 °C? A way is required for filtering out such pure local weather cycles. To easy temperature wiggles in mannequin projections of future local weather, the most recent IPCC evaluation report, AR6, outlined the 1.5 °C mark and different world warming ranges (GWLs) by way of projected 20-year averages relative to the common for 1850–1900. The 12 months of exceedance of a GWL is the midpoint of the 20-year interval at that stage. By this definition, 1.5 °C of warming can be confirmed as soon as the noticed temperature rise has reached that stage, on common, over a 20-year interval — in different phrases, a decade after crossing the 1.5 °C stage. That dangers a delay in recognizing and reacting to the crossing level (see ‘Present world warming ranges’).
Supply: evaluation by R. A. Betts et al.
Researchers and the coverage group must agree urgently on a metric for figuring out the present stage of worldwide warming for coverage functions. As soon as outlined, the metric ought to be formally adopted to be used within the context of the Paris settlement. It ought to be in step with established IPCC practices, and will permit the crossing of 1.5 °C to be acknowledged immediately. Right here, we suggest a place to begin for such a metric.
A number of metrics
In observational information of local weather, the common world temperature over the previous 20 years (2003–22) has been 1.03 °C above that for 1850–1900 (though uncertainties within the information imply that the true worth might be as little as 0.87 °C or as excessive as 1.13 °C; see Supplementary info)2. And measurements from 2002 to 2021 point out that warming first handed 1 °C in 2011. However we don’t know what the 20-year common is now, centred round 2023.
Assuming the world stays on its present warming trajectory, IPCC projections counsel that 1.5 °C shall be breached round 2030, give or take a decade3. However, on the idea of 20-year averages, the passing of 1.5 °C wouldn’t be formally acknowledged till round 2040.
Shortening the interval over which the common is calculated doesn’t assist a lot. Ten-year averages4 are moderately consultant of longer-term averages5 and cut back the delay to 5 years. However that’s nonetheless a very long time when motion is required urgently. Shortening the common interval additional isn’t helpful, as a result of pure variability then dominates.
Local weather loss-and-damage funding: learn how to get cash to the place it’s wanted quick
A extra instantaneous indicator of the present stage of long-term warming is required. A number of such strategies are already in use. These embody: discovering the tip level of a linear pattern over the previous 30 years (see go.nature.com/3ssvpwx); utilizing extra refined strategies for statistical smoothing over quick time frames (see go.nature.com/3mqsr7g); and calculating the human contribution to warming from information on modifications within the concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols6.
Every technique can supply a barely completely different estimate of present warming, relying on which information, algorithms and assumptions are used. Nonetheless, there’s broad settlement on some issues, resembling that warming in 2022 was about 1.24 °C (with an uncertainty vary between 1.0 °C and 1.6 °C), and that 1.0 °C warming was exceeded round 2011 or 2012.
There have been occasions when the variations between strategies had been larger, both as a result of the speed of warming modified quickly so a linear pattern didn’t signify the long-term change, or as a result of massive pure variability led to a distinction between the noticed warming and the human contribution. For instance, there’s much less settlement on the 12 months through which 0.5 °C of warming was exceeded, put at a while between 1982 and 1988. This demonstrates the potential for confusion on recognizing the crossing of 1.5 °C if a single indicator isn’t agreed.
Nevertheless, there are two key issues with utilizing any of those indicators within the context of the Paris settlement. Each stem from the necessity for consistency with current IPCC observe.
Informing coverage
First, to tell coverage, the indicator for monitoring the method to 1.5 °C have to be future-proof — later modifications within the definition may undermine the credibility of utilizing GWLs for scientific recommendation. Any definition have to be in step with how 1.5 °C is already outlined by the IPCC; that’s, utilizing 20-year averages connected to a midpoint.

Corals had been moved to land for security when a July heatwave warmed waters close to Florida.Credit score: Carolyn Cole/Los Angeles Instances through Getty
Second, the metric ought to be in step with how the 1.5 °C stage shall be outlined after it has retreated into the previous — as a baseline for future impression assessments. The IPCC already makes use of long-term averages over current many years for such baselines; it doesn’t use the tip level of 30-year developments or statistical smoothing. And, importantly, baseline intervals for impression research are outlined by way of noticed temperature change, not calculations of human-induced warming, as a result of the impacts depend upon the precise temperature skilled.
The instantaneous metrics are inconsistent with these necessities. And the IPCC technique alone is not going to suffice — 20 years of noticed information is not going to be obtainable within the exceedance 12 months, as a result of it’s only midway via the 20-year interval. One other method is required.
A brand new method
We suggest a brand new indicator — the 20-year common temperature rise centred across the present 12 months. That is estimated by mixing observations for the previous 10 years with local weather mannequin projections or forecasts for the subsequent 10 years, and taking a median over the mixed 20-year interval. This ‘present world warming stage’ (CGWL) indicator meets our two standards — it permits consistency with established IPCC definitions, and offers an instantaneous indicator of present warming.
Local weather loss-and-damage funding: a mechanism to make it work
Testing this method utilizing completely different fashions and emissions eventualities, we’ve got discovered that the CGWL centred on the tip of 2022 is round 1.26 °C, with an uncertainty vary from the forecasts of 1.13 °C to 1.43 °C, primarily owing to local weather variability (see Supplementary info). Solely a small a part of the uncertainty comes from assumptions regarding emissions over the approaching decade7.
This estimate is in keeping with these from the prevailing instantaneous values, however our metric is extra future-proof and in step with the approaches which are already used to help the Paris settlement.
Subsequent steps
First, the worldwide group wants to acknowledge the necessity for a single, agreed metric for crossing the 1.5 °C threshold and anticipate occasions main as much as it. This era shall be marked by a sequence of milestones. These embody: the primary 12 months with a worldwide temperature anomaly above 1.5 °C in a number of information units; the exceedance of 1.5 °C utilizing numerous instantaneous indicators (together with our CGWL metric); and, a decade later, affirmation that 1.5 °C had been exceeded within the IPCC 20-year common.
An instantaneous indicator for coverage functions will present readability that the primary particular person 12 months at 1.5 °C is not going to depend as breaching the Paris guard rail, and can cut back delays that may outcome from ready till the tip of the 20-year interval.
Discussions on the character of this indicator ought to begin instantly.
We encourage the IPCC to sort out this subject in a Particular Report forward of its seventh evaluation report (AR7), which isn’t anticipated to be printed till about 2030 — by which period, world warming may have already got exceeded 1.5 °C or be near doing so.
Catastrophe early-warning methods are ‘doomed to fail’ — solely collective motion can plug the gaps
The IPCC ought to study indicators resembling ours in depth. If an acceptable metric is agreed, a sturdy and clear course of for calculating and speaking it ought to be developed. It ought to make use of well-established sources and practices so far as doable. For instance, observations may come from the WMO’s State of the International Local weather report (go.nature.com/3qqngme), and projections or forecasts may use the IPCC’s assessed warming charges8 and the WMO’s decadal forecasts.
Researchers might want to determine which pathway of future greenhouse-gas and aerosol concentrations ought to be used for the central estimate of the forecast. The selection will want cautious communication, as a result of it might be taken as a press release of an anticipated coverage future, despite the fact that it really makes little distinction compared with uncertainties brought on by pure local weather variability7.
Uncertainties within the mixture of observations and forecasts will have to be quantified extra exactly, and a system for speaking them developed. For instance, formal identification of the passing of 1.5 °C might be accompanied by an IPCC-style confidence or probability assertion — resembling ‘it’s probably that the present world warming stage has now reached (or exceeded) 1.5 °C’. In subsequent years, this may turn into ‘it is extremely probably that the CGWL exceeded 1.5 °C in 12 months X’. This analysis would turn into extra sure as extra observations got here in over the next decade.
Different technical particulars stay to be mentioned. These embody whether or not the projection of the subsequent ten years ought to embody a selected forecast of pure variability (as within the WMO’s decadal forecasts), or whether or not the doable outcomes of variability ought to simply be handled statistically.
We advocate that work start urgently to develop a system to place this definition into use. Researchers should make sure that it’s prepared nicely earlier than the controversy begins over whether or not world warming has exceeded 1.5 °C.





