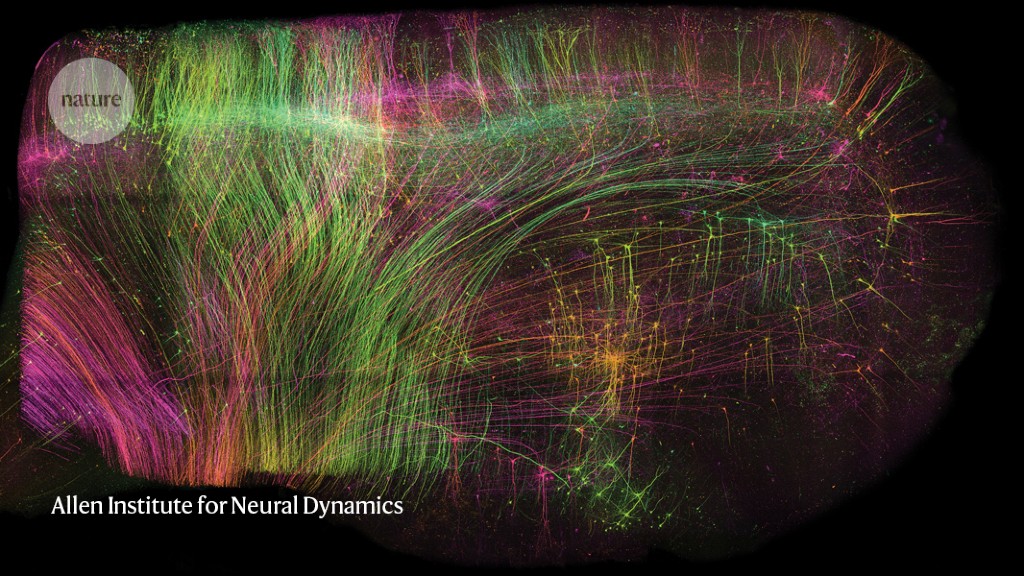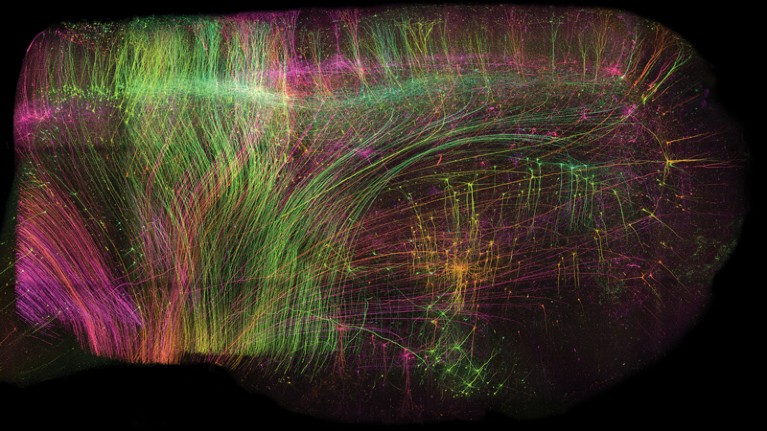
ExA-SPIM imaging of neurons in a bit of macaque mind measuring 1 x 1 x 1.5 centimetres.Credit score: Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics
The mammalian mind is a multiscale system. Neuronal circuitry varieties an info superhighway, with some projections probably stretching dozens of centimetres contained in the mind. However these projections are additionally just some a whole lot of nanometres thick — about one one-thousandth the width of a human hair.
Understanding how the mind encodes and transmits alerts requires the alignment of occasions at each these scales. Conventionally, mind researchers have tackled this utilizing a multi-step course of: slice tissue into skinny sections, picture every part at excessive decision, piece the layers again collectively and reconstruct the paths of particular person neurons.
Zhuhao Wu, a neuroscientist at Weill Cornell Medication in New York Metropolis, describes this final step as “like tracing a phone wire in Manhattan”. In reality, he provides, it’s “much more sophisticated, since each neuron makes hundreds, if not tens of hundreds, of connections”.
Microscope makers have sought to permit researchers to take a wide-angled peek at a big chunk of tissue and nonetheless see the main points up shut, with out having to first slice up the tissue after which reconstruct the axons throughout completely different sections. The problem is that microscope aims are usually designed in such a manner that it’s tough to take high-resolution pictures of huge samples.
A preprint printed in June provides an answer1. First, the researchers chemically eliminated the lipids to make the tissue clear. Then, they embedded it in a fabric known as a hydrogel, which absorbs water, to develop the tissue to 3 occasions its unique quantity. Lastly, they scanned it with a lens borrowed from a totally completely different subject of science. On this manner, it was doable to picture complete mouse brains with out the necessity for any slicing, and at a decision of about 300 nm within the imaging airplane and 800 nm axially (perpendicular to the airplane), akin to that of confocal microscopy, a method extensively used for high-resolution mind imaging. Known as ExA-SPIM (enlargement assisted selective airplane illumination microscopy), the protocol was additionally used to picture neurons in macaque and human brains.
“The large factor that such a system brings is the mixture of with the ability to picture very massive volumes [of brain tissue] at very superb decision,” says Jayaram Chandrashekar, a neuroscientist on the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics in Seattle, Washington, who co-led the examine with two colleagues: microscope developer Adam Glaser and institute head Karel Svoboda.
The strategy can picture a whole mouse mind in below a day — a lot quicker and at greater decision than is feasible with different whole-brain approaches which have been utilized to axon projections, similar to MouseLight and fMost, which use tomography, says Chandrashekar. And the truth that pictures require solely restricted computational reconstruction considerably will increase the accuracy of the ensuing information.
Wu notes that not one of the system’s parts is new — they’re simply assembled in a synergetic manner. “It’s not the primary try to do that however it’s in all probability one of the best try that we’ve got now,” he says.
Step-by-step
The primary aspect of the protocol — tissue clearing and enlargement — has been used for many years, however often on smaller items of tissue. The staff needed to optimize the approach to guarantee that the mind samples develop isotropically — that’s, by the identical quantity in all instructions, says Glaser.
However the coronary heart of the brand new technique is the lens, Glaser says. In selecting it, they seemed to the machine imaginative and prescient and metrology industries, selecting one that’s usually used to determine pixel-sized defects in flat-panel shows and different digital gadgets as they transfer alongside a conveyor belt. The lens has a bigger subject of view than do these usually used within the life sciences, he says, and since the tissue is expanded earlier than imaging, the one-micrometre decision is ample to hint an axon throughout your entire mind.
The researchers constructed that lens right into a microscope that pictures 3D buildings as a sequence of 2D sheets, a method known as selective airplane illumination. They then added a digital camera — additionally taken from the machine imaginative and prescient and metrology industries — that has 38 occasions extra pixels than do cameras conventionally used within the life sciences and might seize a subject of view that measures 10.6 mm × 8.0 mm. With these specs, a 2D sheet of an expanded mouse mind might be captured in about 15 tiles, in contrast with 400 tiles for a standard microscope, Chandrashekar says.
Highly effective microscope captures motor proteins in unprecedented element
“I preferred that they thought exterior the field and seemed into different fields of science,” says Flavie Lavoie-Cardinal, a neuroscientist and microscopist on the College of Laval in Quebec Metropolis, Canada. “That’s manner higher than approaches involving personalized lenses,” she provides, which might make the system much less accessible to different researchers.
Katrin Willig, a microscopist on the Georg-August College of Göttingen, Germany, says ExA-SPIM “is unquestionably of curiosity”, significantly for research of mind connectivity, or ‘connectomics’. However, she provides, “it will be good to enhance the decision a bit additional to have the ability to clearly see dendritic spines.”
Knowledge trove
In response to Glaser, a single mind might be imaged in lower than a day. The staff has to this point imaged 25 or so mouse brains, producing some 2.5 petabytes of information, which the staff compresses five-fold and shops within the cloud. For information evaluation, the researchers collaborate with Google, which gives machine-learning algorithms for processing the information and reconstructing pictures of the neurons.
The quantity of information concerned may characterize a big hurdle for would-be customers, says Hari Shroff, a microscopist at Janelia Analysis Campus in Ashburn, Virginia. Aside from the problem of analysing this quantity of information, simply transferring it from the microscope to a pc is a giant carry, he says. “Consortia of labs or institutes may put money into the folks, the ability or the infrastructure to try this, but it surely’s not trivial to deal with,” he says.
Sensible microscopes spot fleeting biology
That mentioned, the microscope design is open-source and directions for constructing it are obtainable on GitHub. However Glaser says that the present model is a prototype that he plans to streamline and doc over the subsequent yr. “It takes time to assemble, and it’s not super-easy to construct,” he says. To date, a number of labs have expressed curiosity, however none has tried organising the system. “We’re going to redesign and re-engineer the microscope and doc it extraordinarily nicely — and hopefully even obtain funding to disseminate the system in order that different teams can undertake it.”
Tracing long-range neuronal connections is the obvious utility, and it’s the one the researchers are at present pursuing, says Chandrashekar. However they’re additionally transforming the clearing and enlargement protocols to maintain biomolecules similar to RNA and proteins intact, and permit them to be localized as nicely.
“I’m trying ahead to seeing how different basic neuroscience issues may additionally profit from this know-how,” says Wu.