Astronomers introduced on Thursday (Sept. 28) that that they had for the primary time captured the faint glow of the biggest construction within the universe often called the “cosmic net,” a community of filaments that join galaxies throughout the universe. Photos resembling these unveil precious details about how galaxies kind and evolve, and may assist hint the situation of elusive darkish matter that makes up round 80% of the mass within the universe.
In 2014, astronomers imaged the cosmic net for the primary time utilizing radiation from a faraway quasar, distant objects powered by black holes a billion occasions bigger than our solar that are regarded as the brightest objects in the universe. In 2019, one other imaging effort obtained assist from younger, star-forming galaxies to illuminate the encircling cosmic net. Now, astronomers have immediately imaged its mild within the darkest depths of house between 10 billion and 12 billion light-years away.
“Earlier than this newest discovering, we noticed the filamentary constructions beneath the equal of a lamppost,” Christopher Martin, who’s a professor of physics on the California Institute of Know-how and the lead creator of the brand new research, mentioned in a assertion. “Now we are able to see them and not using a lamp.”
Associated: Shockwaves rocking the ‘cosmic net’ connecting galaxies seen for the first time

In response to cosmological simulations, over 60% of the hydrogen that was created by the Massive Bang roughly 13.8 billion years in the past collapsed to kind a sheet, which then broke aside to make the online of cosmic filaments we see at present. These filaments join galaxies and feed them gasoline for development and star formation. Though circumstantial, earlier analysis has additionally urged that galaxies kind the place these threads cross paths.
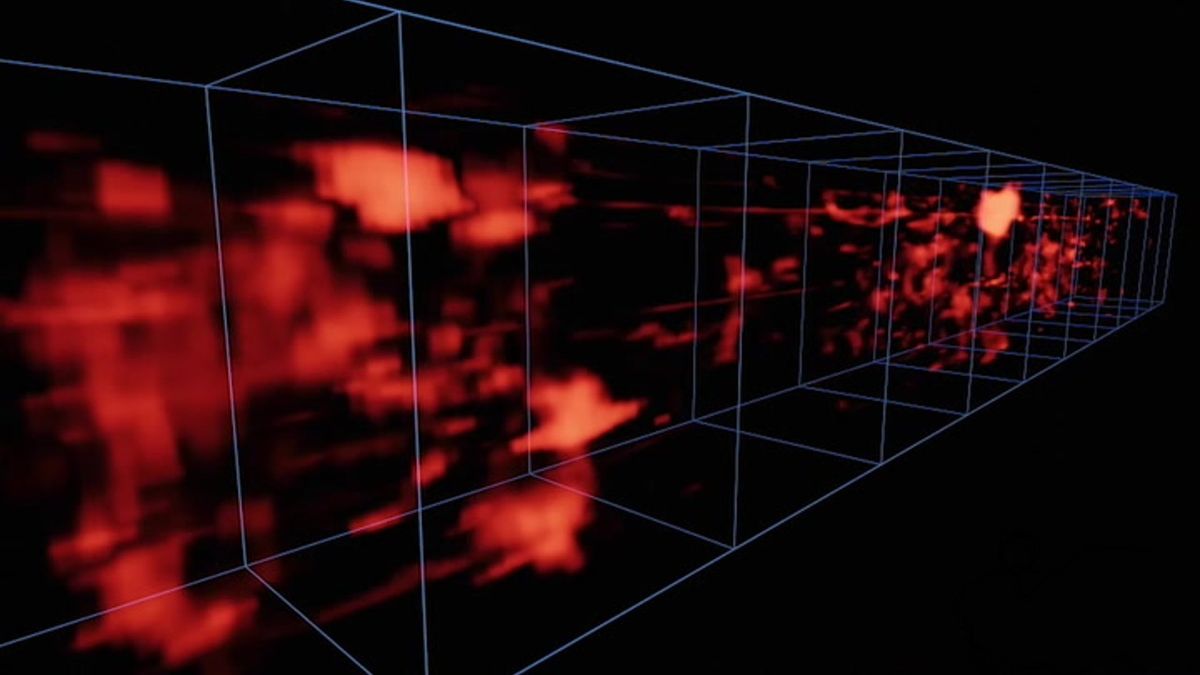
To seize the newest picture of those crisscrossing filaments, Martin and his group used the Keck Cosmic Net Imager based mostly on the Keck Observatory perched atop the Mauna Kea volcano peak in Hawaii. The instrument was tuned to search out emissions from hydrogen gasoline, which is the principle element of the cosmic net. The 2-dimensional pictures produced by the instrument had been later stacked to kind a three-dimensional map based mostly on the place the emissions had been detected as they emanated from the cosmic net, in response to the brand new research.
“We’re principally making a 3D map of the cosmic net,” Martin mentioned in the identical assertion. “We take spectra for each level in a picture at [a] vary of wavelengths, and the wavelengths translate to distance.”
To identify these faint emissions, his group needed to first battle a homegrown downside: Gentle air pollution. The dim mild from the cosmic net can simply be confused with mild permeating within the Hawaiian skies, atmospheric glow and even mild from our personal Milky Method galaxy.
So the group determined to take footage of two completely different patches of the sky by which the cosmic net was thought of to be at distinct distances. Then, the group took background mild from one picture and subtracted it from the opposite, and vice versa. The consequence left behind simply the filamentary community of the online, as predicted by simulations in 2019, in response to the brand new research, giving astronomers “an entire new solution to research the universe,” Martin mentioned.
Scientists say pictures like those captured by the brand new research can assist them higher perceive how galaxies kind and evolve throughout eons.
This analysis is described in a paper revealed Thursday (Sept. 28) within the journal Nature.