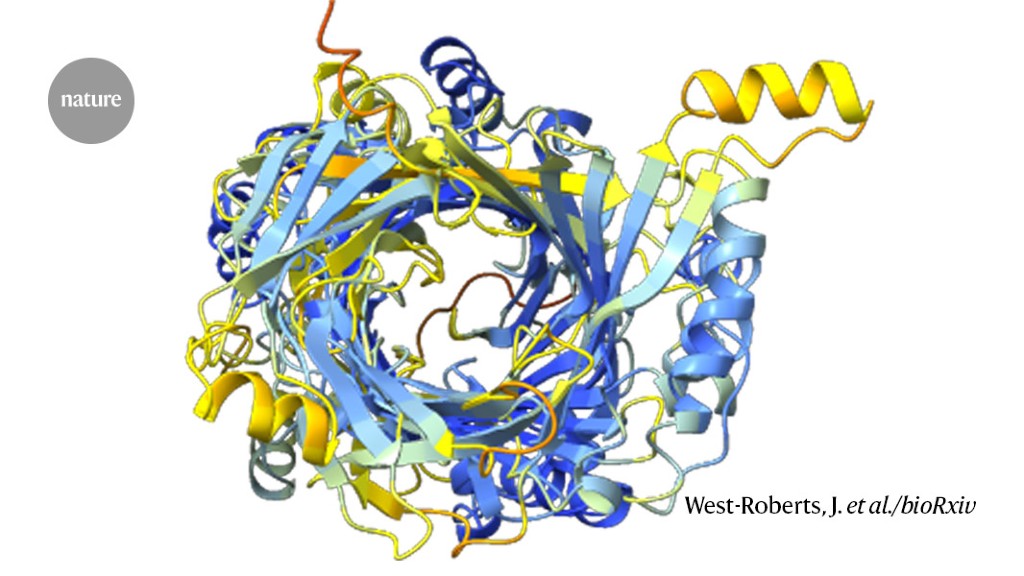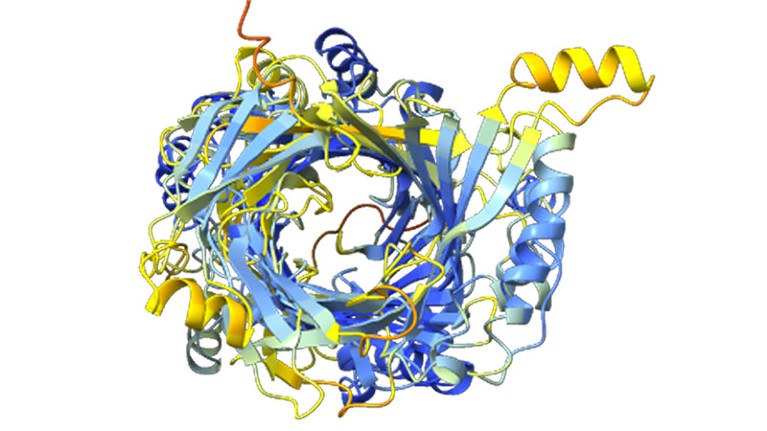
A construction prediction for an enormous protein found by computational biologist Jacob West-Roberts and his colleagues.Credit score: West-Roberts, J. et al./bioRxiv
Jacob West-Roberts, a computational biologist on the College of California (UC) Berkeley, was scouring microbial DNA sequences for large genes and found what he thought was a whopper: a gene encoding a protein made up of 1,800 amino acids. The common protein has a number of hundred.
“Wait until you see this,” responded his PhD adviser, UC Berkeley environmental microbiologist Jillian Banfield, and identified proteins longer than 30,000 amino acids, already recognized from sequencing information.
What’s subsequent for AlphaFold and the AI protein-folding revolution
Their workforce has now discovered dozens of even larger proteins, together with what is perhaps the longest ever: an 85,000-amino-acid behemoth. The mega-molecules might assist an enigmatic group of environmental microorganisms to feed on different microbial cells, the researchers suggest. They describe their findings in a preprint posted on bioRxiv1 final month.
“It’s a superb examine,” says Brian Hedlund, a microbiologist on the College of Nevada, Las Vegas. “They primarily doubled the scale of the biggest recognized predicted proteins from 40,000 to 85,000 amino acids, that are all insane.”
A roughly 35,000-amino-acid protein present in muscle tissues, named Titin, has held the title of world’s greatest protein for many years. However the Guinness World Data won’t should be up to date — but. West-Roberts and his colleagues inferred the existence of their large proteins from gene sequences and predicted components of the molecules’ shapes with the synthetic intelligence (AI) device AlphaFold. It’s potential that, after being made by cells, the enormous proteins get snipped into bits which have totally different features. “You simply don’t know at this level,” says Hedlund.
Hidden giants
The newest complete survey of large proteins was printed2 in 2008. To get a extra updated image, West-Roberts regarded for genes encoding large proteins in public databases and in new genome information from environmental sources, together with a seasonal pond close to Banfield’s dwelling in northern California and a Colorado swamp.
Large proteins had been particularly widespread in Omnitrophota, a bacterial phylum first found in Yellowstone Nationwide Park within the northern United States within the Nineties and now generally present in environmental samples. In whole, the researchers discovered 46 Omnitrophota genes encoding proteins longer than 30,000 amino acids, together with the 85,804-amino-acid-colossus, which turned up in waste water. “They had been simply completely in all places,” says West-Roberts.
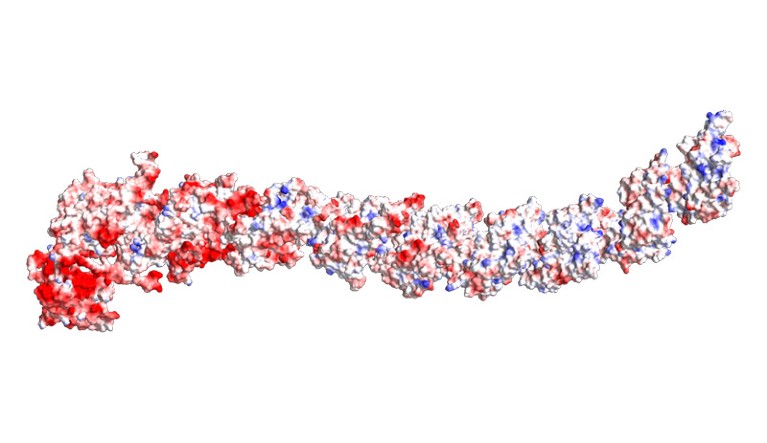
A construction prediction for a ‘Dockerin-type’ large protein, a class coined by West-Roberts’s workforce.Credit score: West-Roberts, J. et al./bioRxiv
Regardless of the microbes’ ubiquity, researchers know little about Omnitrophota, past what could be gleaned from sequences. Largely, it’s because scientists have had little luck rising examples within the lab. However final 12 months, a workforce led by microbiologist Jens Tougher on the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen, Germany, reported a breakthrough3. In wastewater samples that had been incubating within the lab in slow-growing cultures because the Nineties, they discovered cells — small even by microbial requirements — that contained Omnitrophota genetic materials. The workforce developed strategies to counterpoint samples with these cells, after which analysed them.
How AlphaFold can understand AI’s full potential in structural biology
Genome sequencing recognized a gene predicted to encode a protein almost 40,000 amino acids lengthy, and matching protein fragments turned up in a biochemical assay. Tougher’s workforce may even have caught a glimpse of the enormous in electron micrographs of the Omnitrophota cells, which appeared to point out them attacking and devouring different micro organism and microbes known as archaea.
Protein predators
To find out whether or not the enormous proteins West-Roberts had found are concerned in comparable predation, he and his workforce tried to check the sequences utilizing computational strategies designed for determiningwhat a lot smaller proteins do. “These instruments will not be made for large proteins. They simply don’t know what to do with them,” he says.
Regardless of these challenges, the workforce managed to be taught a bit concerning the titans. Lots of the proteins appear to wind their manner by means of the mobile membrane a dozen or extra instances. A lot of the enormous proteins embody sequences that resemble these of enzymes that connect to and break up sugars and different biomolecules discovered on cell partitions. These might be used to bind and digest the cell partitions of prey, the researchers recommend.
To attempt to discover out what a few of the large proteins appear like, West-Roberts and his colleagues plugged parts of their sequences into AlphaFold, Google DeepMind’s revolutionary protein-structure-prediction device. However the community isn’t outfitted for proteins bigger than a few thousand amino acids, so the researchers break up their mega-proteins into overlapping 1,000-amino-acid stretches. “If you happen to make it too lengthy, AlphaFold will simply type of surrender in some unspecified time in the future and provide you with a ball of spaghetti,” says West-Roberts.
The AI predictions of the proteins’ buildings revealed extra cell-wall-binding areas, but in addition an enormous shock: a really lengthy tube-like equipment in contrast to something researchers have ever seen. This construction might be concerned in delivering molecules to prey, or might connect to different cells earlier than the host microbe devours them.
Martin Steinegger, a computational biologist at Seoul Nationwide College, is impressed with how the researchers made sense of the mega-molecules utilizing AlphaFold and different cutting-edge instruments. “Having the ability to annotate such large molecular equipment past the capabilities of conventional strategies marks a considerable leap ahead,” he says.
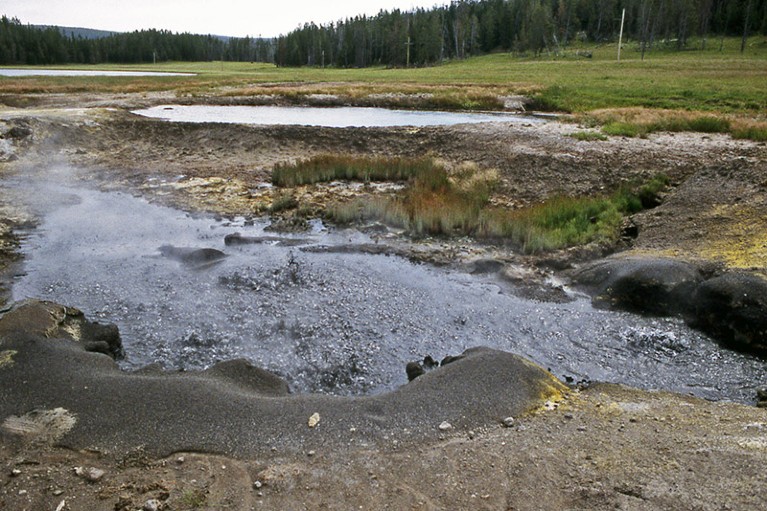

The Obsidian Pool in Yellow Stone Nationwide Park, the place a bacterial group that hosts large proteins was found.Credit score: Bob Lindstrom/American Nationwide Park Service
The truth that large proteins are so widespread in Omnitrophota is particularly shocking due to the microbes’ tiny bodily measurement, says Oleg Reva, a bioinformatician on the College of Pretoria in South Africa. The examine reveals that big proteins are “subtle weapons wielded by the diminutive microbial hunters of their pursuit of bacterial and archaeal prey”, he provides.
Actual-world existence
The invention of genes encoding proteins as longer than 85,000 amino acids doesn’t imply that the molecules exist on this state in cells, researchers say. One risk is that the protein is chopped into smaller items after it’s made, and these parts tackle a variety of features in cells. That might clarify why Tougher’s workforce was capable of finding solely items of its large protein. “At the moment I don’t see experimental proof that these massive proteins exist,” Tougher says.
Lots of the large proteins comprise protein-breaking enzymes known as peptidases, which might chop the Goliaths down into Davids, West-Roberts and his workforce say. Agency solutions may require researchers to develop Omnitrophota cells, one thing that solely Tougher’s workforce has managed to take action far. “All of the others, they’re simply imaginary,” says Tougher. “There’s a variety of thriller to resolve.”
West-Roberts will get his PhD quickly, and he’s received different tasks to tie up, together with a examine of large proteins in archaea. He would like to see others examine the enormous proteins he has discovered, and he desires of somebody figuring out what they actually appear like utilizing experimental methods equivalent to cryo-electron microscopy or a associated methodology that may map proteins in cells. “I simply actually wish to see it and get a floor fact of what it truly is,” he says. “It will be such a cool picture.”